Over-the-Counter (OTC) Hearing Aids
Are you interested in hearing aids, but don’t want to pay a lot of money to try them? If so, then you are not alone!
As an Auditory Neuroscientist, I can assure you that our current model of hearing healthcare delivery is inadequate in addressing the needs of our hearing-impaired population. For whatever reason (access, costs, cosmetics, etc.), only 20%-25% of those who need hearings aids in the United States actually have them. This means that our current hearing healthcare model misses 75%-80% of hearing-impaired patients who need hearing aids. Clearly, we need better options to reach those of us who have difficulty hearing in quiet situations or hearing in the presence of background noise.
In 2015, the Obama Administration suggested that the Federal Drug Administration approve a low-cost option for hearing aids whereby the hearing-impaired consumer could purchase hearing aids without seeing a physician or hearing healthcare provider (PCAST Recommends Changes to Promote Innovation in Hearing Technologies | whitehouse.gov (archives.gov)). The goal was to eliminate barriers so more hearing-impaired persons can access the hearing healthcare they need. The Trump Administration continued this policy and directed the FDA to approve the first over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids, and then the FDA approved the first OTC hearing aids in 2023 during the Biden Administration (Hearing Aids | FDA).
The conclusions from the administrations are summarized in the following video: https://youtu.be/f3jCxzJaa-A.
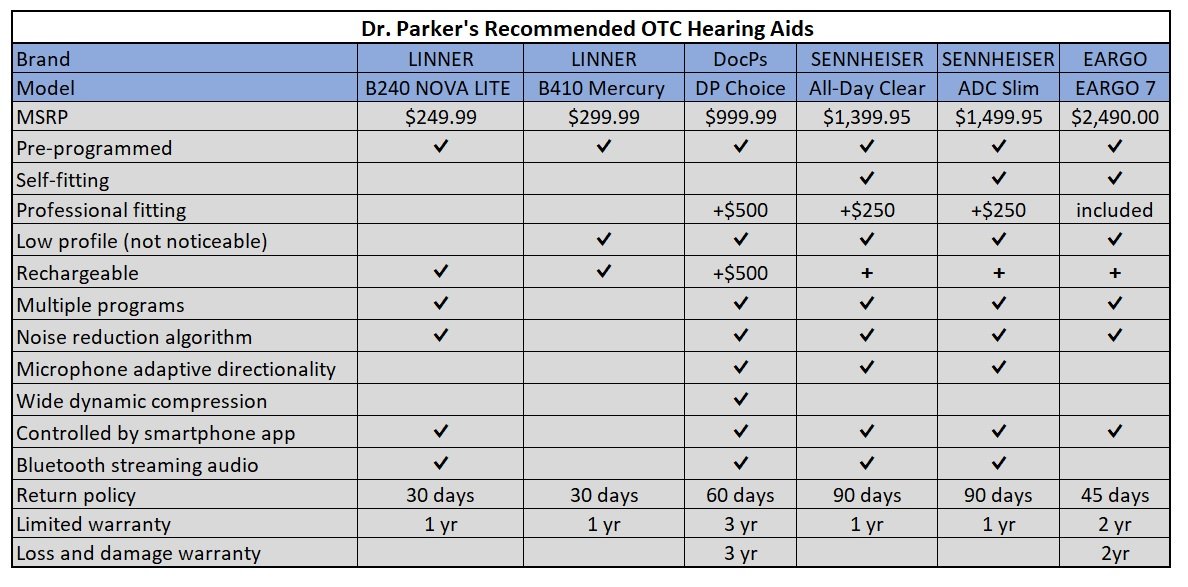
It’s a good thing that OTC hearing aids are available at Walmart, pharmacies, the internet, etc. However, considering the plethora of OTC hearing aids available to you, which OTC hearing aids are the best? Which are worth a chance? And which are worthless?
We have evaluated all of the readily available OTC hearing aids on the market (Agenda 2023 — Palm Springs Hearing Seminars (palmspringshearingseminars.com)) and have concluded that some OTC hearing aids are worthless, some are cheap yet effective options, and some are very good and relatively inexpensive options for the hearing impaired. A list of recommended OTC hearing aids can be found in the STORE.
In general, OTC hearing aids can be divided into three categories based on their output (or programming):
Pre-programmed: These are typically less expensive and the output is programmed for someone with a “typical” hearing loss. In essence, they are guessing that you have an average degree and type of hearing loss, and their output would provide you with some benefit. Some of the better models in this class may have different pre-programmed outputs and will allow you to choose the program that best suits your needs.
Self-fitting: These are more expensive and typically offer both pre-programming and an option to customize the hearing aid output to match your individual hearing loss. For the customized output, you will take a hearing test through the smartphone application and the hearing aid output will be optimized for your individual hearing loss.
Professional fitting: These are self-fitting hearing aids that a hearing healthcare professional (i.e. Technician, Hearing Instrument Specialist, or Audiologist) can program in case other programming options are ineffective. In some cases, an online technician who is trained in programming the specific device will assist you, and in other cases your regular audiologist will have that capability.
If you are interested in OTC hearing aids and have any questions, please contact me to discuss the best options for you or your loved ones.
I would love to help you!
Mark A. Parker, PhD, CCC-A
Please be aware that all of these OTC hearing aids are FDA approved for adults (18+) with perceived mild to moderate hearing loss and they do not require a visit to an audiologist or a hearing test.